How to Reclaim Hard Drive Space by 'Shrinking' Windows 10
Windows 10 has a smaller footprint than earlier versions of Windows, but if you have a Windows tablet or laptop with a small storage drive, every byte counts. Here are three ways to make Windows take up less room on your hard drive or SSD.
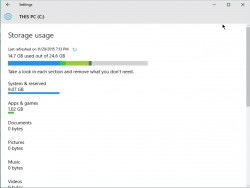
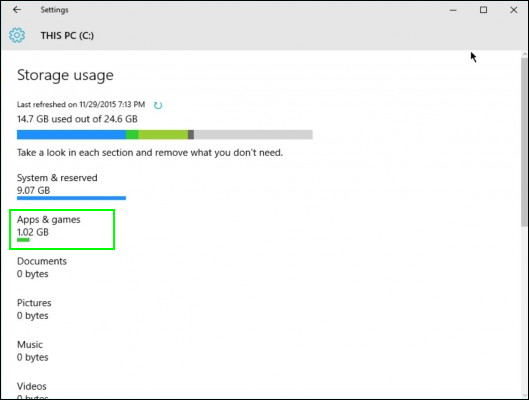
A fresh install of Windows 10 takes up about 15 GB of storage space. Most of that is made up of system and reserved files while 1 GB is taken up by default apps and games that come with Windows 10. This might not sound a lot, but if you have a cheap 32GB Windows laptop or even a 64GB one, it's a significant portion of your storage space taken up by the operating system. For example, the Lenovo Ideapad 100S comes with just 32GB of internal memory and only 17GB of free space out of the box. You can reduce Windows's footprint by uninstalling default Windows 10 apps, disabling the hibernation, and tweaking the virtual memory settings. All of these strategies work in previous versions of Windows, except for uninstalling Windows 10 default apps.
How to Uninstall Default Windows 10 Apps
[windows-space-apps]
The apps that come pre-installed with Windows 10 don't take up much space individually, but they add up and also clutter the Start menu. Uninstall the ones you don't need.
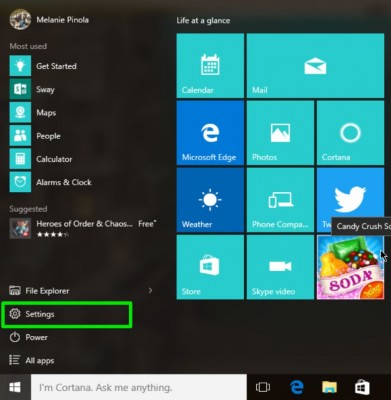
1. Open Settings from the Start menu.
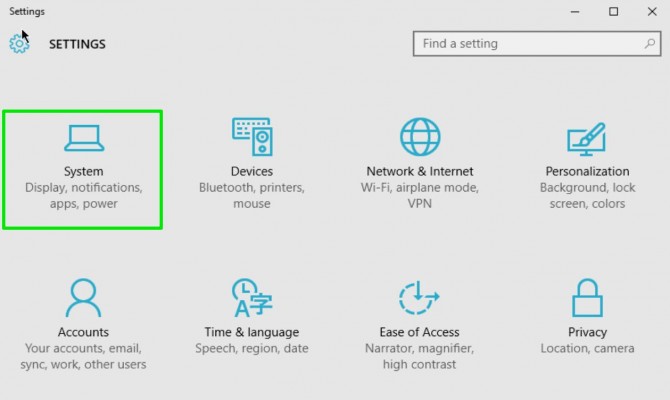
2. Click System.
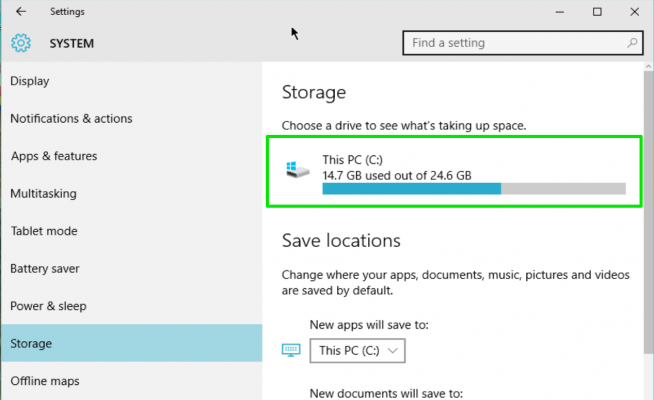
3. Click on Storage and then in the right pane select your C: drive.
Sign up to receive The Snapshot, a free special dispatch from Laptop Mag, in your inbox.
[
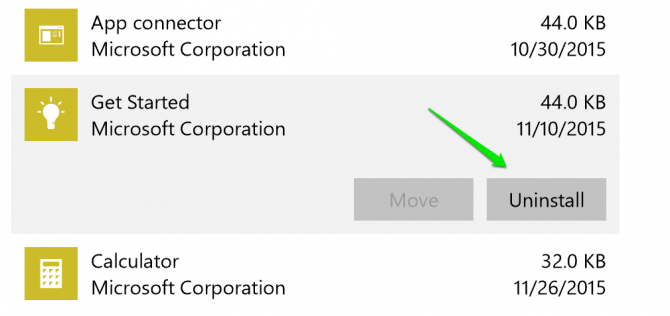
4. Click on Apps & features.
5. Click on an app and then the Uninstall button to uninstall the app.
Some apps, such as Groove Music and Xbox, Mail and Calendar, Maps, and Xbox can't be uninstalled from here. You have to use Powershell commands to get rid of them. See the full list of Powershell commands to use at How-To Geek
Turn Off Hibernation
When you hibernate your computer, Windows saves your computer's current state--your open documents and programs--to your storage drive so you can resume your work when you turn the computer back on. If you don't use hibernation mode, you can disable it and get rid of the hiberfil.sys file, which takes up several gigabytes of storage space.
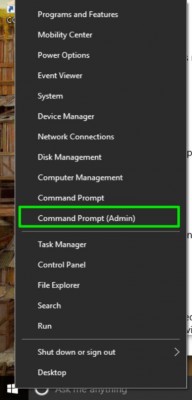
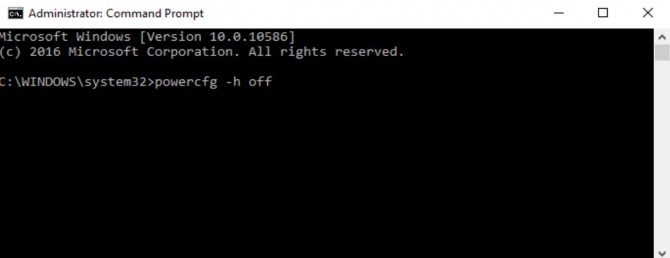
1. Open a Command Prompt in Administrator Mode by right-clicking on the Windows Start button and choosing Command Prompt (Admin).
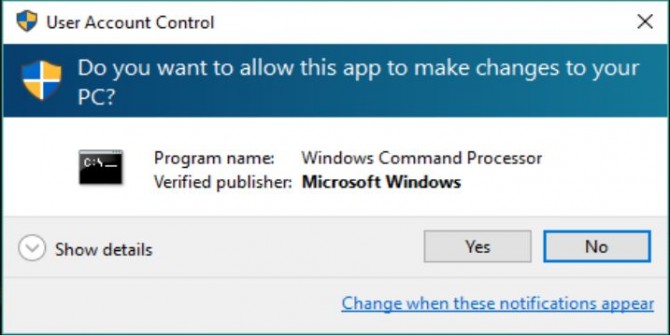
2. Click Yes if User Account Control asks whether to allow the Command Prompt to open.
3. In the Command Prompt window, type in powercfg -h off and hit Enter.
This will delete the hiberfil.sys file on your computer and remove the option to hibernate your system. You can still put your computer to sleep, which saves your computer state to memory instead of your hard drive and keeps your computer on but in a low-power state.
Change the Virtual Memory Size in Windows 10
With virtual memory, if your computer doesn't have enough physical memory to run a program or operation, Windows will temporarily move some data from RAM to a paging file on your hard drive. You can limit how much space this paging file takes up.
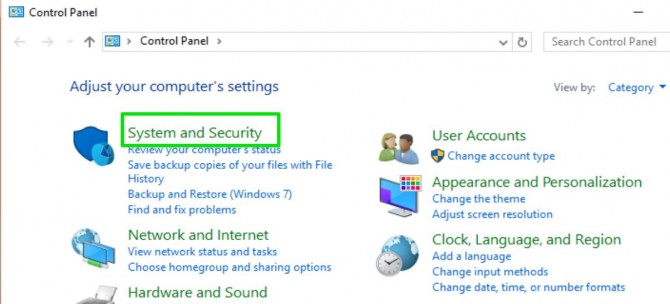
1. Open the Control Panel. You can do this by searching for it on the taskbar or start menu.
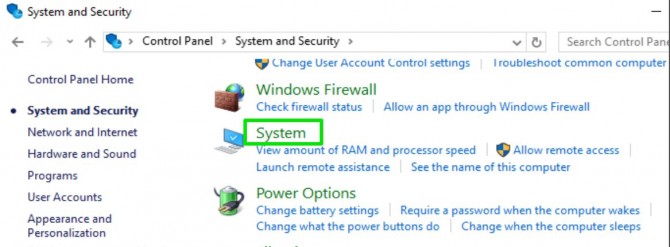
2. Click System and Security.
3. Click System.
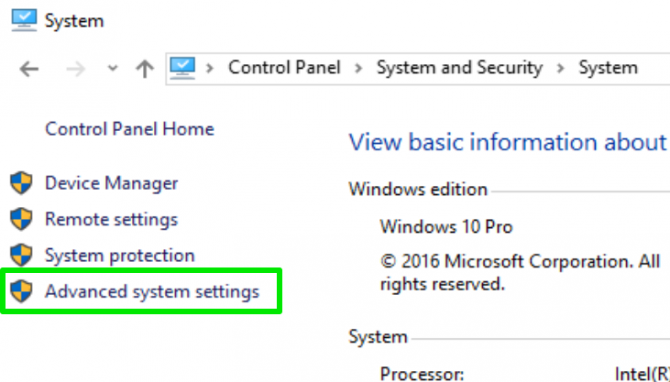
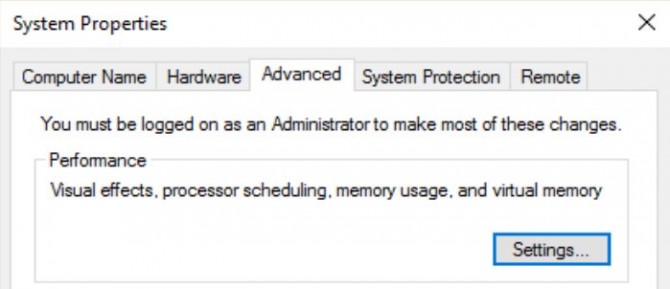
4. Click on Advanced system settings in the left menu.
5. Go to the Advanced tab and click the Settings button under the Performance section.
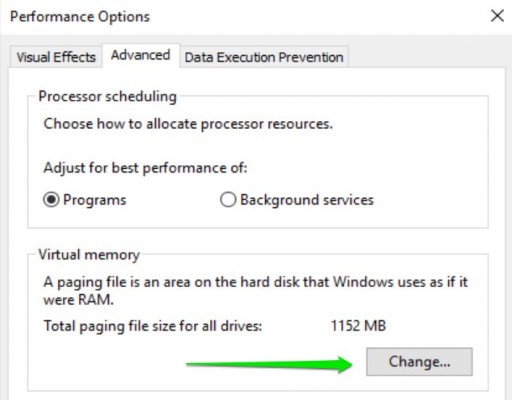
6. Go to the Advanced tab and click the Change… button in the Virtual memory section.
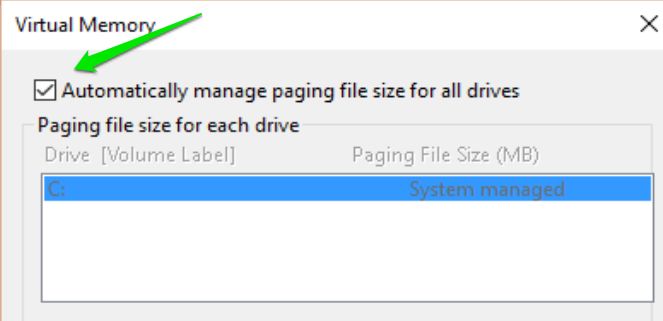
7. Uncheck the box next to "Automatically manage paging file size for all drives".
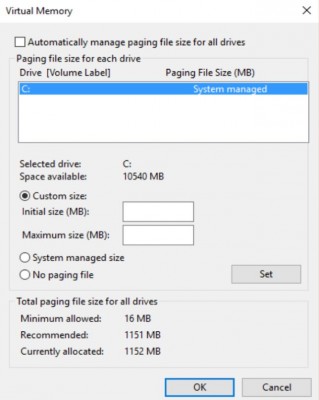
8. Select the "Custom size" option and enter the initial and max sizes you wish to let the file grow to. Hit Set and then OK to finish.
(Alternatively, you can select "no paging file" or leave the system to manage the file size, but for performance reasons you should have a paging file).
The steps above could free up several gigabytes of space on your hard drive by limiting how much space Windows takes up on your computer.
Windows 10 Storage and Backup
- Reclaim Hard Drive Space by Shrinking Windows 10
- Delete the Windows.old Folder in Windows 10
- How to Save Space By Cleaning Windows' WinSxS Folder
- Back Up Files with the File History Feature
- Mount and Burn ISO Files
- Format a Hard Drive For Both Windows and Mac
- Zip a File or Folder in Windows 10
- Control Which OneDrive Files Are Available Offline
- Map OneDrive as a Network Drive
- Fetch Any File on a Remote Computer with OneDrive
- 3 Ways to Save Space
- Free Disk Space Automatically with Storage Sense
- All Windows 10 Tips
- How to Install Apps to an External Drive
Melanie was a writer at Laptop Mag. She wrote dozens of helpful how-to guides, covering both the software and the hardware side of things. Her work included topics like SSDs, RAM, Apple, Excel, OneDrive, and detailed guides for Windows users. Outside of all her useful advice, Melanie also penned a few reviews for Laptop Mag, including Android emulators that help you run apps on your PC.